Embedded Motion Control 2018 Group 5: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 72: | Line 72: | ||
==Software Architecture== | ==Software Architecture== | ||
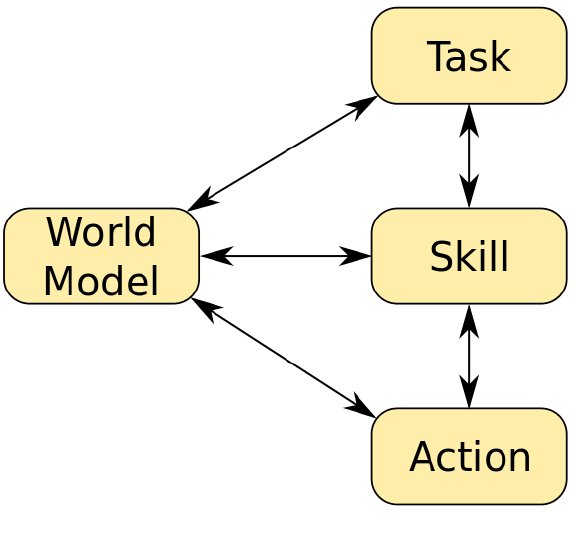
[[File:EMC2018SCHEMA.png|thumb|right|350px|Software architecture [3]]] | [[File:EMC2018SCHEMA.png|thumb|right|350px|Software architecture [3]]] | ||
Tasks: | |||
* Navigate | |||
Skills: | |||
* Go straight | |||
* Go backwards | |||
* Turn left | |||
* Turn right | |||
Actions: | |||
* Laser scan | |||
* Move motor | |||
Choices to be made/questions to be answered: | Choices to be made/questions to be answered: | ||
Revision as of 15:18, 5 May 2018
Group information
| Name | Student number | |
|---|---|---|
| M.J.W. Verhagen | 0810317 | m.j.w.verhagen@student.tue.nl |
| L.W. Feenstra | 0847751 | l.w.feenstra@student.tue.nl |
| A.J.J. Steinbusch | ... | a.j.j.steinbusch@student.tue.nl |
| J.T. Galen | ... | j.t.v.galen@student.tue.nl |
Introduction
This project consists of two challenges: the Escape Room challenge and the Hospital challenge. The Escape Room challenge will be an intermediate challenge that serves as preparation of the final challenge which is the Hospital challenge. In both challenges a robot has to fulfill a task autonomously.
The Robot: PICO
The robot that will be used for this project is PICO which is a telepresence robot from Aldebaran from the type Jazz.
- Sensors:
- Laser Range Finder (LRF)
- Wheel encoders (odometry)
- 170 degrees wide-angle camera (cannot be used during the project)
- Actuators:
- Holonomic base (omni-wheels)
- Pan-tilt unit for head
- Maximum speed is 0.5 m/s translational and 1.2 rad/s rotational
- Computer:
- Intel I7
- Running Ubuntu 16.04
Escape Room challenge
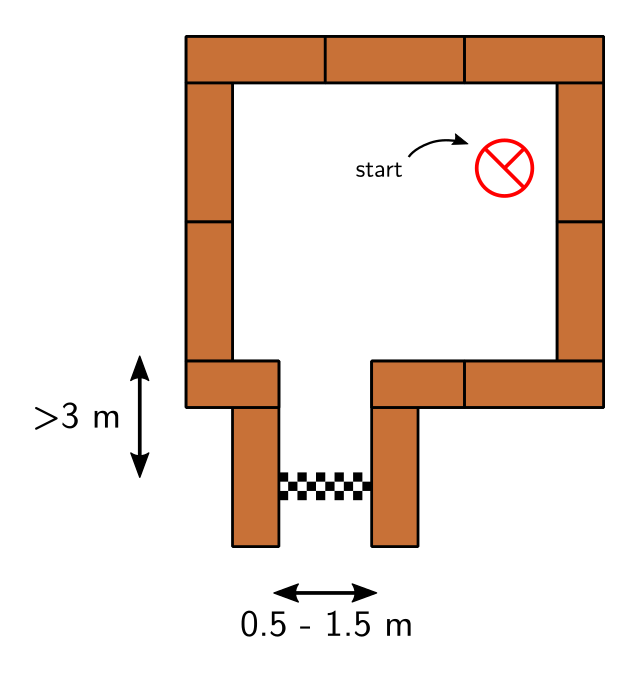
The goal of this challenge is to let PICO escape a room through a corridor as fast as possible. The challenge is completed when PICO has steered itself autonomously with its entire rear wheel over the finish line at the end of the corridor without hitting any walls. PICO will be placed at a random location in the room. To detect the walls the Laser Range Finder can be used. An example of a possible escape room is given below. The escape room of the challenge does not have to be identical to the one below.
The shape of the room will be rectangular, but the length and width of the room will not be known beforehand. It must be taken into account that the walls might not be perfectly straight, nor perfectly perpendicular and parallel to other walls. The width of the corridor will be in between 0.5 and 1.5 meters and the finish line will be more than 3 meters into the corridor to give PICO so more time to align with the walls of the corridor.
Hospital challenge
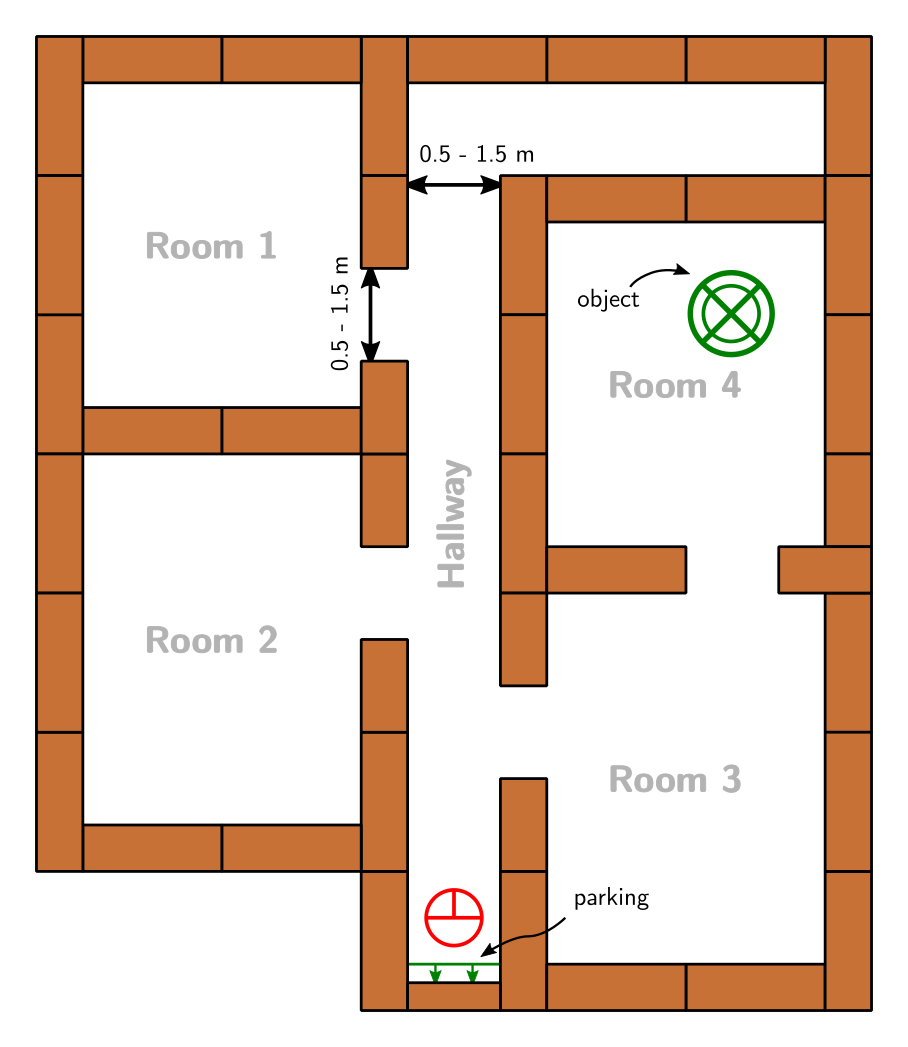
The goal of this challenge is to let PICO find an object in one of the rooms of the hospital as fast as possible and without hitting any walls. Beforehand, PICO will explore the hospital to build a map that will be used to find the object later. After the exploration PICO will park itself backwards to the wall in the halfway which will be its starting position for the search for the object. PICO will search for changes in the map and will recognize that the map has changed at the position of the object. Here it will stop and stand close to the object. Then the challenge is completed. An example of a possible hospital is given below. The hospital of the challenge does not have to be identical to the one below.
The hospital will contain 3 to 6 different rooms. The rooms can be either entered via a hallway or via other rooms. The width of the hallway will be in between 0.5 and 1.5 meters.
Software Architecture
Tasks:
- Navigate
Skills:
- Go straight
- Go backwards
- Turn left
- Turn right
Actions:
- Laser scan
- Move motor
Choices to be made/questions to be answered:
- Of how many laser beams do we want to process the data in which situation? Only 2 can detect a straight line..
- Do we want the robot to move a certain distance from the wall?
- What is the width of the robot?
- From how far can the Laser Range Finder detect a wall? Can we rotate the robot around its z-axis and detect the whole room at once? Probably not.
- What sample time do we want to use?
- Do we leave the room after measuring three corners? Or two? Maybe there are multiple exits...
- How do we explore? If no wall is detected always go left and follow the wall?
- How do we know that we are back at the begin position? The encoder data?
- After creating the map of the hospital plan ideal routes?
[1] Kuijpers, W., EMC 2018 Tooling and Infrastructure (2018). Eindhoven University of Technology Department of Mechanical Engineering
[2] Douven, Y., Houtman, W., Hendrikx, Chen, H.L., B., Farahani, M.D., Kuijpers, W., Bruyninckx, H., Van de Molengraft, R., Embedded Motion Control 2018 (2018). http://cstwiki.wtb.tue.nl/index.php?title=Embedded_Motion_Control
[3] Huebel, N., Bruyninckx, H. Embedded Motion Control Best Practices in System Design for Robot Control (2017). Mechanical Engineering KU Leuven & TU Eindhoven