Embedded Motion Control 2017 Group 6: Difference between revisions
| Line 85: | Line 85: | ||
** Distance between walls can range from 0.5 to 1.5 meter | ** Distance between walls can range from 0.5 to 1.5 meter | ||
** Distance from start to finish is between 1 and 10 meters | ** Distance from start to finish is between 1 and 10 meters | ||
** Start is located between the walls in the main corridor | |||
** Finish is located 0.3 meter inside a side corridor on either the left or right | ** Finish is located 0.3 meter inside a side corridor on either the left or right | ||
** Main corridor has | ** Main corridor has open ends | ||
* Maze challenge | * Maze challenge | ||
** Maximum of two attempts within 7 minutes total | ** Maximum of two attempts within 7 minutes total | ||
Revision as of 11:47, 30 May 2017
About the group
| Name | Student ID | |
|---|---|---|
| Ties Hoenselaar | 0857112 | t.a.h.hoenselaar@student.tue.nl |
| Hasan Ilisu | 0852221 | h.h.ilisu@student.tue.nl |
| Laura de Jong | 0743679 | l.s.d.jong@student.tue.nl |
| Lars Moormann | 0861223 | l.moormann@student.tue.nl |
| Bas Straatman | 0777325 | s.r.t.straatman@student.tue.nl |
| Jeroen van der Velden | 0744957 | j.r.v.d.velden@student.tue.nl |
| Wouter Houtman | Tutor | w.houtman@tue.nl |
Introduction
The most memorable part of the course Embedded Motion Control is the 'A-MAZE-ING PICO' challenge, in which software is designed for and implemented into autonomous robots. These autonomous robots, called Pico and Taco, should then be to able to solve a maze with the software in a real-life environment. A maze can contain loops, dead ends, open spaces and doors that automatically open and close.
Pico will be provided with a basic software layer to carry out primary functions, such as communication and movement. However, to succesfully complete the 'A-MAZE-ING PICO' challenge it is required to design robust software for the changing environment. Several software subsystems will be put to the test in an intermediate challenge. During this challenge, called the corridor competition, Pico must move through a corridor and take the first exit. With the results of the corridor competition and all its software subsystems Pico should be able to finish the maze challenge. The course Embedded Motion Control is concluded with an overall conclusion.
Software design
The ever-changing environment in reality requires the design of a robust software architecture. It is prefered to design this software architecture before actually programming, because it gives a clear understanding/agreement of the different functions from the start. The first step in creating the software architecture is to mention the requirements that have to be met in order to complete the corridor competition and the maze challenge. Pico should be able to finish these challenges succesfully by using most of its components. Secondly, a list of specifications will be given to accuratly describe the robot, corridor and maze. With these requirements, components and specifications it is then possible to define functions for the software architecture. The software architecture is completed by specifying the interface between these different functions.
Requirements
To complete the corridor competition and maze challenge Pico has to meet the following requirements:
- Operate fully autonomous
- Avoid collisions with walls
- Robust against sensor disturbances and layout imperfections
- Update, compile, start and end software with single commands
- Corridor competition
- Move through a corridor that complies with the specifications
- Exit the corridor within the set time limit
- Recognize junctions
- Maze challenge
- Move through a maze that complies with the specifications
- Escape the maze within the set time limit
- Recognize junctions, loops, dead ends and doors
- Ring the bell at dead ends and doors
- Stand idle for a certain period of time
Components
The following components of Pico will be used to fulfill the requirements:
- Sensors
- Laser range finder (LRF) determines the distance to an object with a laser beam
- Wheel encoders (odometry) determine the position of Pico relative to a starting position
- Actuators
- Holonomic base with three omni-wheels to drive and turn
- Bell to request a door to open
- Computer
- Intel I7 processor
- Ubuntu 14.04 as operating system
Specifications
Pico, the corridor competition and the maze challenge are characterized by the following specifications:
- Pico
- Dimensions of ?? x ?? x ?? (LxWxH)
- Maximum translational speed of 0.5 m/s
- Maximum rotational speed of 1.2 rad/s
- Maximum amount of bell actions equal to the amount of doors plus dead ends
- Maximum idle time of 30 seconds
- LRF
- Located at ??
- Range of ??
- Horizontal field of view of 270°
- Frequency of ??
- Accuracy of ??
- Odometry
- Located at ??
- Resolution of ??
- Frequency of ??
- Accuracy of ??
- Corridor competition
- Maximum of two attempts within 5 minutes total
- Penalty of 5 seconds or 1 attempt when slightly touching or bumping a wall
- Corners are approximately 90°
- Walls are approximately parallel to each other
- Distance between walls can range from 0.5 to 1.5 meter
- Distance from start to finish is between 1 and 10 meters
- Start is located between the walls in the main corridor
- Finish is located 0.3 meter inside a side corridor on either the left or right
- Main corridor has open ends
- Maze challenge
- Maximum of two attempts within 7 minutes total
- Penalty of 5 seconds or 1 attempt when slightly touching or bumping a wall
- Corners are approximately 90°
- Walls are approximately parallel to each other
- Distance between walls can range from 0.5 to 1.5 meter
- Distance from start to finish is unknown
- Start is located inside the maze, but outside a door area
- Finish is located beind the door on the boundary of the maze
- Can contain loops, open spaces and more tha one dead end
- Contains one door and is located at a dead end
- A dead end is a wall with a length of between 0.5 and 1.5 meter with side-walls of at least 0.3 meter
- A door area is the area 1.3 meters in front of the door
- Door opens when Pico is inside the door area, stands still and sends a request
- Door starts opening within 2 seconds and is opened within 5 seconds
- Door opens to the left or right with approximately constant velocity
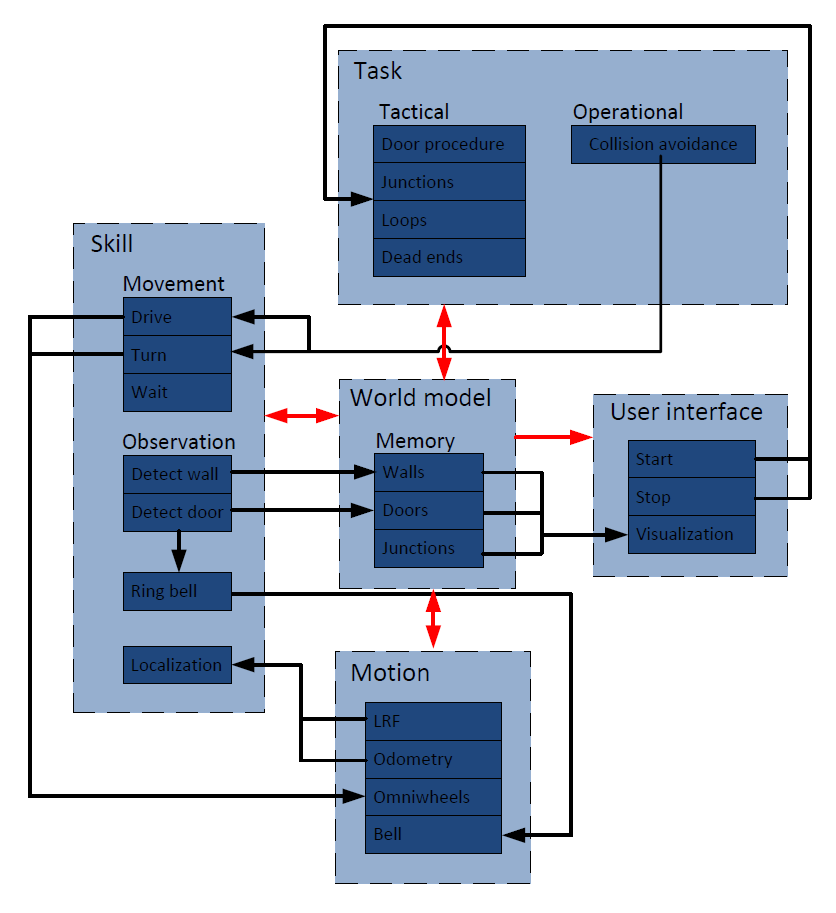
Functions
The software must have the following functions in order to meet the requirements and fulfill the goal:
| Function: | Description |
|---|---|
| Drive forward | The robot must drive forward unless something, for
example a wall or a corner, is detected |
| Drive backward | The robot must drive a little bit backward if it is unable to rotate |
| Turn left | Make a 90degree left turn |
| Turn right | Make a 90degree right turn |
| Ring bell | The bell must be rang in order to open the door |
| Localize | The robot has to localize itself in the world model, because the
odometry data isn't that accurate |
| Wait | The robot must wait at a dead end in order to check if it is a
door |
Interfaces
The main relations between the interfaces are colored red and can be described as follows:
World model -> Task:The world model can give information about taken paths to the Task
World model -> Skill:The stored observations in the world model are used for movement skills
World model -> Motion:The world model can give data to the actuators
World model -> User interface: The user interface needs the data from the world model to visualize the world model to the human
Task -> World model:The task needs to store information about paths in world model
Skill -> World model :The world model is build from observations
Motion -> World model :The motion can give sensor data about the position to the world model
File:Initial design plan EMC group 6.pdf