Summary Chiel van der Laan: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
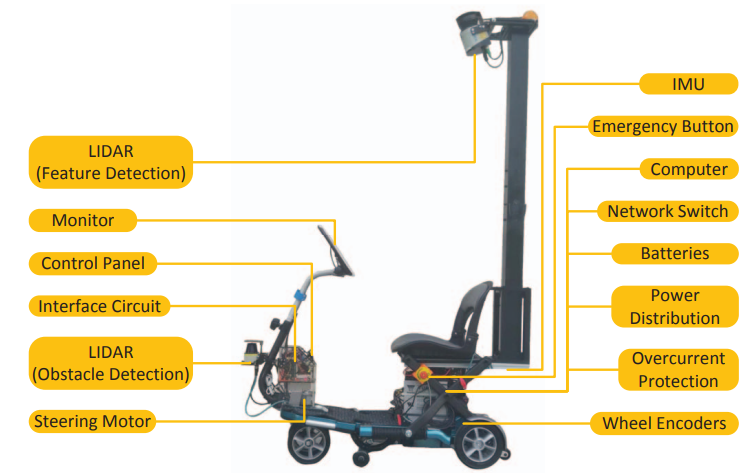
The problem of mapping can be solved by constructing a 2D scan with a LIDAR system from a 3D environment. [1] After which it the localization can be done in the 2D mapped environment for lower processing power.[2] An example of the visual validation of localization can be seen in figure 1. The LIDAR system for the mapping and localization has to be able to scan a large area at once and has to be high on top of the mobility scooter because of this. | |||
[http://www.example.com (1)] | [http://www.example.com (1)] | ||
[[File:Mobility scooter.png]] | [[File:Mobility scooter.png]] | ||
Revision as of 15:39, 18 February 2018
The problem of mapping can be solved by constructing a 2D scan with a LIDAR system from a 3D environment. [1] After which it the localization can be done in the 2D mapped environment for lower processing power.[2] An example of the visual validation of localization can be seen in figure 1. The LIDAR system for the mapping and localization has to be able to scan a large area at once and has to be high on top of the mobility scooter because of this. (1)