PRE2018 3 Group12
Introduction
| Name | Study | Student ID |
|---|---|---|
| Harm van den Dungen | Electrical Engineering | 1018118 |
| Nol Moonen | Software Science | 1003159 |
| Johan van Poppel | Software Science | 0997566 |
| Maarten Flippo | Software Science | 1006482 |
| Jelle Zaadnoordijk | Mechanical Engineering | 1256238 |
The wiki page is divided into five sections: exploration, requirements, design, implementation, and conclusion. These five sections represent the five phases of the project.
Exploration
This section defines our chose problem, the background of this problem, and our approach to tackle it.
Problem Statement
In 2011, almost 302.000 people in the Netherlands have a visual handicap. [1] They can either be visual impaired or totally blind, but in both cases the person needs help. This number of people was 302.000, but now, and in the future this number will grow. This is because of the fact that the Netherlands are dealing with an aging society. The average age of people is rising. Now is that not especially a bad thing, but the body of people is breaking down during the years. And so are their eyes. The older a person gets, the bigger the chance is that he or she gets visual impaired and in the worst case even blind. Until now there isn’t found a way to prevent it from happening, so we just have to deal with it.
We have a growing number of 302.000 people in our society that have problems with their eyes. But not only those people are the ones that have to deal with it. Also family members and friends want to do the best for their loved ones. Because they didn’t choose for their flaws and maybe they did the same for them in the past. Everyone want the best for everyone, but what is the best in this moment?
We know that people with a visual impairment will never be able to sense the world as people without visual impairment. But there are some ways to make their lives more comfortable. Thanks to guide dogs and canes these people are able to enjoy independence when it comes to navigating in outside areas. They can enjoy a walk with the dog, without having a person telling them what to do or where to walk. This suppresses the feeling of dependency of such a person. They can walk when and where they want to. Although this is now the best way to deal with the impairment, it isn’t completely flawless. With the cane you’ve got the problem of the range of the cane. The person only knows what is happening in this range, but nothing that is happening outside of it. The same problem with the dog, because it only makes sure that the person moves around with hitting any pole or something. So the dog only looks at the movement of the person in small distances. Both tools help the person to have an idea of what around him, but only in between a curtain range. They don’t get a full representation of how the rest of world looks like.
With the use of technology that might change. Using sensors these people could be given the ability to sense more than their immediate surroundings, sense objects which their white cane didn't contact or the dog ignored because it was not in the way. Also, using physical phenomena such as the Doppler effect one can also detect motion relative to you, further enhancing the image a visually impaired person can obtain of the world.
USE aspects
User
When designing a product, the most important thing to know is for who we are creating the product. This target group of people is called users. In the early years designers developed a product in the way only they themselves thought best. <source?> History has shown us that developing products in this way is not the most efficient way. <source?> When developing a product based only on what you think is best, it is easy to miss certain aspects. This is possible, but not necessary, that this results in great problems. Developing a new product without a clear view on your future users increases the chance of developing a product fit for nobody. This is not efficient moneywise and timewise. We can draw the conclusion that it is necessary to take the user into account, when developing a product. In the next two sections we answer the following questions: who are our users and what do they want, and how are we going to satisfy all the needs of our users?
Identifying the users and their needs
The primary users we are designing the technology for, are visually impaired people. Almost 302.000 people in the Netherlands are visually impaired. This is, in our eyes, a large amount of the population. For a blind or partially blind person, even the simplest tasks can be hard to complete. A walk for some fresh air can be a really hard task for someone that cannot orientate himself in the area in which he or she is unfamiliar. For those tasks they often require aids. Those aids are in most cases a guidance dog, or a white cane. By using those aids, the visually impaired can get those tasks done. He or she still cannot orientate himself or herself, but he or she can figure out where objects are. This is, of course, already a nice improvement the situation where these persons did not use these aids. However, in our opinion there still is a lot to improve, because (like stated in the problem statement) those aids have their flaws. By using the existing aids the user can avoid a car but do not know that the object the user is avoiding, is a car. When the dog drags the user away from the car, or his cane hits the car, the user now knows that he has to avoid something, but not what. What our design aims to create for the primary user, is a better impression of how the world looks and works. Improving the living experience of our primary users is our main target.
The secondary users are the friends, family and maybe the caretaker of the primary user. These people are close to the user and assist the primary user if something does not work out as planned. For example, when the primary user cannot take the guidance dog to the veterinary, the second user assists him or her. The most important aspect that we need to take into account is: how do you want to bring that info to the secondary user and is that everything that the secondary user needs? To get this information, it is possible to use scenarios. This to define every possible outcome and in turn, the different problems that can come up. In this way, we get an idea of which problems there may be, that we did not take into account the first time. After obtaining those possible problems, we have to find a way how the second user can assist to overcome those problems. It needs to be simple for the second user, because every one of the secondary users have to be able to fix it.
Satisfying the user needs
Now that we have identified our users and their needs, we look at how we are going to satisfy these needs. As stated before, we want to know what our users like of our concept, and what they would like to see changed. There is no better way to get this information than to get it directly from our primary and secondary users. We want to contact several of our users and ask them about our concept. Through this survey we want to come to know if our concept is a concept that they would like use. Only after we know this information, we can determine whether we can proceed with our concept, or rethink it entirely. We have an image of what the user would like to see, and know how to create a product that our user would like to use. Now maybe the most difficult part has to happen, combining the concept with his technology with the users wishes. The most important requirement of the final product is that it offers a valid alternative to existing aids. This does not necessarily mean that the technology better support the users disability than alternatives, it could also mean that it is simply cheaper. If the product is cheaper it can still be an option for people not able to afford more costly alternatives. There are many factors classifying the value of a product. Two important factors are the production and selling costs, and the support given and the usability of the technology.
Society
Like mentioned before, nowadays almost 302.000 people in the Netherlands are dealing with a visual impairment. That’s around 3% of the population of the Netherlands. 3% doesn’t seems to be such a great number, but almost everyone knows someone with a visual impairment. Maybe it’s the neighbor or maybe it’s your own mother or father. Although there is a difference in how much you care about those people. Everyone deserves to live their lives as good as they want to, and to support them in this we have to support them in their flaws. If your mother can’t walk anymore then you take here everywhere in an wheelchair, but with a visual impairment you can’t just buy new eyes or something. And by this you can’t get the same end product. The only thing that is possible for this flaw in our time is to make their life more complete. To get as close as possible to that same end product.
The most of our population now tries to avoid the visual impaired people in public. This can have the reason that we don’t want to interrupt them in focusing how to come around. But also with the fact that it is possible to think that visual impaired people don’t know that we are there, so why interrupt them. Everyone can have another reason but in most cases it leads to giving the visual impaired person space. Whatever reason a person has it doesn’t matter it gets the same outcome. The visual impaired person is getting treated in a different way than a person with a healthy sight. This can give mixed feelings, because in most cases we as society only try to help. This help is always welcome, but the other side of this is that visual impaired people most of the time want to be treated as equals. To be as equals we’ve to get as close as possible to realizing that end result. That’s where our concept comes in. Our concept gives the visual impaired person the feeling of what is happening around him and may give him more the feeling of being part of the society. He or she now knows that someone is walking beside of him and maybe want to start a conversation with him/ her. The visually impaired person is less dependent and can do more on its own. Also the society will react less extreme on an visual impaired person, because with our concept it won’t as noticeable that the person is visual impaired as with a cane or dog.
Our concept won’t have any influence on the society further on. This is because our concept would replace the cane or the dog and doesn’t need any attachments in an area. So there aren’t beacons or camera’s needed in the city which would have an influence on the society. Our concept only an influence on the living experience of the visual impaired person and on the second users that need to learn how to attach the belt and assist as further needed. Those second users are in most cases already the people that assist the visual impaired person in what they need. For them almost nothing changes only the fact that they see the primary person as an happier person with the same input that they always have given.
Like said before we can’t get to the same end product, because the technology won’t let us to. But by our concept we are extending the possibilities of visual impaired people without bothering the society in a major way. We only ask the second user to assist the primary user, but in most of the times this is already the case. They will know everything that is around them and what is moving around them. So they are closing up on the end product and that’s our goal.
Enterprise
The enterprise aspect of equipment for the handicapped is a complicated one. This is because the target demographic is, more often than not, dependent on government alimony programs, or health insurance. The reason for this is that these people commonly are not able to provide for themselves, due to their handicap. [2] This complicates the enterprise aspect, since the final product has to comply with several government and health insurance restrictions.
Some of these restrictions (in the Netherlands) include:
- People can only get one device per category from their health insurance. These categories are reading, watching television, and using a computer. These restrictions are imposed by health insurers, the reasoning behind this is that one device is enough. The problem with this restriction is that it is possible for one device to fall into two categories, or two completely different ones to fall into the same. For example, a device for enlarging a physical newspaper falls in the same category as an electronic magnifier for mobile use. [3]
- Companies that manufacture devices to aid blind people and of which the devices are covered by health insurance, cannot advertise with their products. [4]
- Health insurers do not like to cover proprietary devices, as these devices commonly are more expensive than cheaper ones containing older technology. [4] This is beneficial for insurers as it cuts costs.
These rules and restrictions have a great impact on the final product, and the success of the final product. A product can be perfect in every way, but if it does not comply to these written and unwritten rules, it may never reach the hands of the people that need it most. Even if the goal of the company making the products is not to make money, an can price the products as low as possible, the price can still be too high for the users to afford it without help of the health insurance.
State of the Art
After doing some initial exploration, we found that the problem can be subdivided into two sub problems: how the environment can be perceived to create data, and how this data can be communicated back to the user. Now follows a short summary of existing technologies:
Mapping the environment
Many studies have been conducted on mapping an environment to electrical signals, in the context of supporting visually impaired users. This section will go over the many different technologies that these studies have used. These method can be subdivided into two categories: the technologies that scan the environment, and those who read previously planted information from the environment.
One way of reading an environment, is to provide beacons in this environment from which an agent can obtain information. In combination with a communication technology, it can be used to communicate this geographical information to a user. Such a system is called a geographic information system (GIS), and can save, store, manipulate, analyze, manage and present geographic data. [5] Examples of these communication technologies are the following:
- Bluetooth can be used to communicate spatial information to devices, for example to a cell phone. [6]
- Radio-frequency identification (RFID) uses electromagnetic fields to communicate data between devices. [7]
- Global Positioning System (GPS) is a satellite based navigation system. GPS can be used to transfer navigation data to a device. However, it is quite inaccurate. [7][8]
The other method of reading an environment is to use some technology to scan the environment by measuring some statistics. Examples of these scanning technologies are the following:
- A laser telemeter is a device that uses triangulation to measure distances to obstacles.[9]
- (stereo) Cameras can be used in combination with computer vision techniques to observe the environment. [10][11][12][13][14][15][16]
- Radar or ultrasound are high frequency sound waves. A device sends out these sounds and receives them when they reflect on objects. This is used to calculate the distance between sender and object. [17][18][19][20][21][22][23][24][8][25][26][27][28]
- Pyroelectricity is a chemical property of materials that can be used to detect objects.[27]
- A physical robot can be used in combination with any of the above mentioned techniques, instead of the device directly interacting with the environment. [29]
Communicating to the user
Given we are dealing with the visually impaired, we cannot convey the gathered information through a display. The most common alternatives are using haptic feedback or audio cues, either spoken or generic tones.
Cassinelli et al. have shown that haptic feedback is an intuitive means to convey spatial information to the visually impaired [28]. Their experiments detail how untrained individuals were able to dodge oncoming objects from behind reliably. This is of great use as it shows haptic feedback is a very good option of encoding spatial information.
Another way to encode spatial information is through audio transmissions, most commonly through an earbud for the wearer. An example of such a system was created by Farcy et al. [9]. By having different notes corresponding to distance ranges this information can be clearly relayed. Farcy et al. make use of a handheld device, which caused a problem for them. It required a lot of cognitive work to merge the audio cues with where the user pointed the device. This made the sonorous interface difficult to use so-long as the information processing is not intuitive. In this project the aim is to have a wearable system, which could mean this problem is not of significance.
Finally, regardless of how distance is encoded for the user to interpret, it is vital the user does not experience information overload. According to Van Erp et al. [30] users are easily overwhelmed with information.
State of the Art conclusion
From our State of the Art literary study, we conclude that a wide variety of technologies have been used to develop an even wider variety of devices to aid visually impaired people. However, we noticed relatively little papers focus on what is most important: the user. Many papers pick a technology and develop a product using that technology. This in and of itself is impressive, but too often there is little focus on what this technology can do for the user. Only afterwards a short experiment is conducted on whether or not it is even remotely usable by the user. Even worse, in most cases, not even visually impaired users are the ones that test the final product. The product is tested with blind-folded sighted people, but differences exist that a blindfold cannot simulate. Research has shown that the brains of blind people and sighted people are physically different[31], which could lead to them responding differently to the feedback that the product provides. The fact that the user is not involved in the early stage of decision making, leads to the fact that the final product is not suited for the problem. When the problem is fully understood by involving the actual users, a product can be developed solving the problem.
Approach
To follow our State of the Art conclusion, our goal is to design a system to aid blind people that is tampered to the needs of this user from the ground up. That is why we aim to involve the user from the start of the project. Firstly, we are first going to conduct a questionnaire-based research to fully understand our user. Only after understanding the user, we will start to gather requirements to make a preliminary design that fills the needs of thse users. After the preliminary design is finished, building the prototype can be started. During the making of the design and building the prototype, it is probable that some things might not go as planned and it will be necessary to go back steps, to make an improvement on the design in the end. When the prototype is finished, it is tweaked to perform as optimal as possible using several tests. We also aim to actually test the final prototype with visually impaired people. Finally, everything will be documented in the wiki.
Deliverables and Milestones
A prototype that aids blind people roaming around areas, that are unknown to them. This prototype is based on the design of last year[32]. From this design, a new design was made that tries to improve on the issues the previous design faced. Additionally, a wiki will be made that helps with giving additional information about the protoype, such as costs, components and it provides some backstory of the subject. Finally, a presentation is made regarding the final design and prototype.
- Presentation
- Presentation represents all aspects of the project
- Design
- Preliminary design
- Final design based on preliminary design, with possible alterations due to feedback from building the prototype
- Prototype
- Finish building the prototype regarding the final design
- Prototype is fully debugged and all components work as intended
- Prototype follows requirements
- Must haves are implemented
- Should haves are implemented
- Could haves are implemented
- Wiki
- Find at least 25 relative state-of-the-art papers
- Wiki page is finished containing all aspects of the project
Planning
| Week | Day | Date | Activity | Content | Comments |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Week 1 | Thursday | 07-02 | Meeting | First meeting, no content | |
| Week 1 | Sunday | 10-02 | Deadline | Finding and summarizing 7 papers | |
| Week 2 | Monday | 11-02 | Meeting | Creating SotA from researched papers | |
| Week 2 | Tuesday | 12-02 | Deadline | Planning, users, SotA, logbook, approach, problem statement, milestones, deliverables | Edited in wiki 18 hours before next panel |
| Week 2 | Thursday | 14-02 | Panel | ||
| Week 2 | Sunday | 17-02 | Deadline | Prioritized and reviewed requirements document | |
| Week 3 | Monday | 28-02 | Meeting | Discussing previous deadline (requirements) | |
| Week 3 | Thursday | 21-02 | Panel | ||
| Week 3 | Sunday | 24-02 | Deadline | Preliminary design | |
| Week 4 | Monday | 25-02 | Meeting | Discussing previous deadline (preliminary design) | |
| Week 4 | Thursday | 28-02 | Panel | Maarten not present at panel | |
| Vacation | Sunday | 10-03 | Deadline | Final design | Final design is based on preliminary design |
| Week 5 | Monday | 11-03 | Meeting | Discussing previous deadline (final design) | |
| Week 5 | Thursday | 14-03 | Panel | ||
| Week 6 | Monday | 18-03 | Meeting | Discussing deadline progress (prototype) | |
| Week 6 | Thursday | 21-02 | Panel | ||
| Week 6 | Sunday | 24-03 | Deadline | Prototype complete | |
| Week 7 | Monday | 25-03 | Meeting | Discussing previous deadline (prototype) | |
| Week 7 | Thursday | 27-03 | Panel | ||
| Week 7 | Sunday | 31-03 | Deadline | Conclusion, discussion, presentation | |
| Week 8 | Monday | 01-04 | Meeting | Discussing what is left | |
| Week 8 | Thursday | 04-04 | Final presentation |
Findings from visiting Zichtbaar Veldhoven
On Thursday 21 February Jelle, Harm and Nol went to Zichtbaar Veldhoven. Zichtbaar Veldhoven is a small association for the visual handicapped. On the date of visiting, a presentation took place about currently available aids. The presentation was given by a representative from a company specialized in this equipment. The most notable findings are the following:
- The target demographic is dominated by the elderly. A visual handicap is also an illness that comes with the ages. This is something we had not taken into consideration. It is very important however, because people in this demographic more often suffer from more illnesses that influence the design: partially hearing, tremors, and a general lack of knowledge of technology.
- The market for aids for the visually impaired is vastly complicated. These people are dependent on insurance, and the insurance companies are reluctant on buying proprietary equipment due to costs.
These findings are worked out in more detail in their respective sections. References to findings from this visit are stated with "Personal communication with..".
Requirements
This section contains the requirements for the product, as well as the approach of gathering these.
Getting information from the intended users
To get information from the intended users, we have decided to contact a few foundations for visually impaired people. We asked them if we can interview them, or even better some members of their foundation. The questions we have asked them (in dutch):
- Wat zijn obstakels in het leven tijdens het navigeren en hoe zouden deze opgelost kunnen worden?
- Hoe doet u dit bij onbekende locaties?
- Welke hulpmiddelen heeft u nu al?
- Wat zou u graag willen waarnemen wat u niet al krijgt met de huidige hulpmiddelen?
- Stel dat u objecten die dichtbij zijn zou kunnen waarnemen?
- Stel dat u de beweging van objecten kunt waarnemen?
- Heeft u baat bij technologie die u extra ondersteund om te lopen op (onbekende) location?
- Waar zou u het comfortabel vinden om sensoren te dragen?
- Zou het voor u uitmaken als het apparaat zichtbaar is?
- Stel we hebben dit product, dan zal er ergens een batterij in moeten zitten. Op welke manier zou het voor u duidelijk zijn hoe u dit moet aansluiten?
- Waar kunnen we het beste rekening mee houden met het ontwerpen van ons product?
- Zou u bereid zijn om extra geld uit te geven voor deze techniek?
- (Eventueel: Hoe veel?)
- Mochten wij in dit vak zo ver komen om een werkend prototype te maken, zou u bereid zijn om het uit te proberen?
Design
This section gives an in-depth description of how a product is created that conforms to the requirements.
Simulation of the sensor field of view
One of the goals for this project is to come up with a solution for the limited field of view of the prototype from last year's group. In order to do that, a proposed solution is to have the sensors rotate, enlarging their field of view. Since we want to minimize the amount of rotation whilst maximizing objects detected, we created a simulation in order to test multiple configurations.
Setup
The simulation is a top-down view of the subject and the environment in front of them. Since the human body is roughly approximated by an ellipses from that perspective, the sensors will be mounted on an elliptical curve at the bottom of the window, facing to the top of the window. The sensors are presumed to be spaced evenly across the curve. According to the spec-sheet of the ultrasonic sensor used by last years group, the field of view of each sensor is at most 15 degrees [33] between 2cm and 5m, so that is what will be the field of view per sensor in the simulation as well. Finally, to simulate the user moving forward, rectangles of random dimensions will be randomly initialized at the top of the screen and move towards the bottom at 5 km/h, which is the average walking speed of a human.
Variables
The variables of the simulation are:
- The number of sensors in use: ranges from 1 to 10, 1 being the minimum number of sensors needed to measure anything, and 10 being the maximum number of sensors which make sense considering we are only measuring the area in front of the user.
- The speed of rotation: ranges from 0 rad/s to ? rad/s.
- The amount of rotation: ranges from 0 degrees to 180 degrees, 0 degrees being no motion and 180 degrees being the maximum angle required to scan the whole area in front of the user.
- The phase difference per sensor: ranges from 0 to 360 degrees.
- Note: this is for each sensor from left to right, thereby creating different scanning motions for each sensor.
Measurements
When running the simulation, the following data will be collected:
- How fast each object is detected (distance), once the object is less than 5 meters away from the user.
- How much electricity is required to run the sensors and the servo's.
Designing the prototype
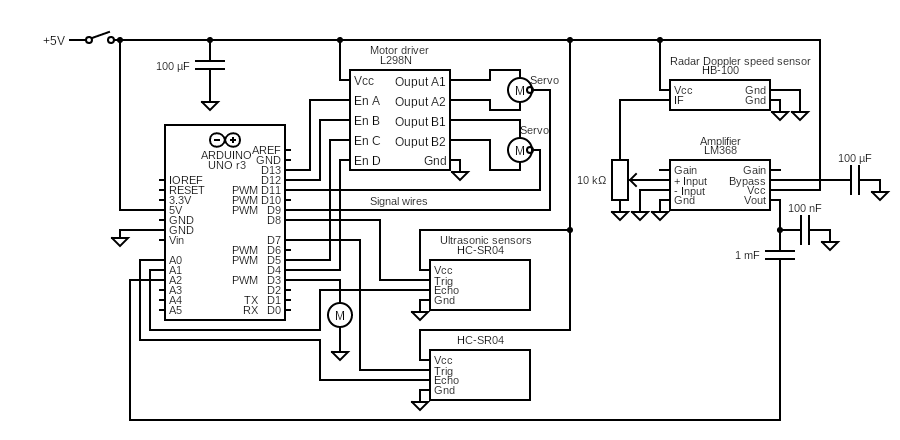
The figure above represents the combined product of both the radar and the ultrasonic parts. In the Design a 100 μF capacitor is added between ground and Vcc. This capacitor will make sure no spike voltage is present when flipping the switch on or off. The capacitor makes the voltage and thus the current increase/decrease slowly to its supposed level. It does not leak any current as the system is operating at DC and a capacitor has infinite resistance at a constant voltage. Furthermore, there are 2 servos on which the ultrasonic senors will be mounted. From this can the results of the simulation be tested. Moreover, a radar Doppler speed sensor is added as well, which outputs an audio frequency based on the Doppler shift. The amplitude of this frequency wave is too small to connect it directly to an audio output, so it is amplified first using an LM368 amplifier. The potentio meter at the front of the amplifier is used as an voltage divider to change the input voltage of the signal. This way, the output amplitude can be chosen to a specific value by turning the potentio meter. Finally, the output is filtered using a low-pass filter by means of the 100 nF capacitor. This is done to attenuate the noise, which is present at high frequencies and makes sure only low frequency sounds (lower than 150 KHz) are going into the audio output. Although the noise is at a higher frequency that the audible region, it can still provide uncomfortable audio signals.
Implementation
Here comes a detailed description of the implementation phase.
Conclusion
Here come the results, conclusion, improvements, etc..
References
- ↑ Volksgezondheidenzorg.info, Accessed on 25-02-2019, https://www.volksgezondheidenzorg.info/onderwerp/gezichtsstoornissen/cijfers-context/prevalentie-incidentie#node-aantal-mensen-met-gezichtsstoornissen
- ↑ Personal communication with stichting Zichtbaar, 21 February 2019
- ↑ Drie tips voor het aanvragen van een hulpmiddel bij uw zorgverzekeraar, nl.optelec.com, Accessed 25-02-2019, https://nl.optelec.com/3+tips+voor+het+aanvragen+van+een+hulpmiddel+bij+uw+zorgverzekeraar
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 Personal communication with representative of Optelec, 21 February 2019
- ↑ Faria, J., Lopes, S., Fernandes, H., Martins, P., & Barroso, J. (2010). Electronic white cane for blind people navigation assistance. World Automation Congress (WAC), 2010, 1–7. Retrieved from https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/abstract/document/5665289/citations#citations
- ↑ Bohonos, S., Lee, A., Malik, A., Thai, C., & Manduchi, R. (2007). Universal real-time navigational assistance (URNA). In Proceedings of the 1st ACM SIGMOBILE international workshop on Systems and networking support for healthcare and assisted living environments - HealthNet '07
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 Fernandes, H., Costa, P., Filipe, V., & Hadjileontiadis, L. (2010). STEREO VISION IN BLIND NAVIGATION ASSISTANCE. 2010 World Automation Congress. Retrieved from https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/abstract/document/5665579
- ↑ 8.0 8.1 Ghate, A. A., & Chavan, V. G. (2017). SMART GLOVES FOR BLIND. IRJET, 12(04), 1025–1028. Retrieved from https://www.irjet.net/volume4-issue12
- ↑ 9.0 9.1 Farcy, R. Bellik, Y. (2002). Locomotion Assistance for the Blind. https://link.springer.com/chapter/10.1007/978-1-4471-3719-1_27
- ↑ Dunai, L., Fajarnes, G. P., Praderas, V. S., Garcia, B. D., & Lengua, I. L. (2010). Real-time assistance prototype- A new navigation aid for blind people. In IECON Proceedings (Industrial Electronics Conference) (pp. 1173–1178). IEEE. https://doi.org/10.1109/IECON.2010.5675535
- ↑ Truelliet, S., & Royer, E. (2010). OUTDOOR/INDOOR VISION-BASED LOCALIZATION FOR BLIND PEDESTRIAN NAVIGATION ASSISTANCE. International Journal of Image and Graphics, 10(04), 481–496. https://doi.org/10.1142/S0219467810003937
- ↑ L. Dunai, G. P. Fajarnes, V. S. Praderas, B. D. Garcia and I. L. Lengua, "Real-time assistance prototype — A new navigation aid for blind people," IECON 2010 - 36th Annual Conference on IEEE Industrial Electronics Society, Glendale, AZ, 2010, pp. 1173-1178. http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/stamp/stamp.jsp?tp=&arnumber=5675535&isnumber=5674827
- ↑ Schwarze, T. Lauer, M, Schwaab, M. Romanovas, M. Böhm, S. Jürgensohn, T. (2015). A camera-based mobility aid for visually impaired people. https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s13218-015-0407-7
- ↑ Wang, H. Katzschmann, R. Teng, S. Araki, B. Giarré, L. Rus, D. (2017). Enabling independent navigation for visually impaired people through a wearable vision-based feedback system. https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/abstract/document/7989772
- ↑ Yi, C., Flores, R. W., Chincha, R., & Tian, Y. (2013). Finding objects for assisting blind people. Network Modeling Analysis in Health Informatics and Bioinformatics, 2(2), 71–79. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13721-013-0026-x
- ↑ Zeb, A., Ullah, S., & Rabbi, I. (2014). Indoor vision-based auditory assistance for blind people in semi controlled environments. In 2014 4th International Conference on Image Processing Theory, Tools and Applications (IPTA) (pp. 1–6). IEEE. https://doi.org/10.1109/IPTA.2014.7001996
- ↑ A wearable assistive device for the visually impaired. (n.d.). Retrieved February 11, 2019, from http://www.guidesense.com/en/
- ↑ Pereira, A., Nunes, N., Vieira, D., Costa, N., Fernandes, H. & Barroso, J. (2015). Blind Guide: An ultrasound sensor-based body area network for guiding blind people. Procedia Computer Science, 67, 403–408. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procs.2015.09.285
- ↑ Al-Mosawi, Ali. (2012). Using ultrasonic sensor for blind and deaf persons combines voice alert and vibration properties. Research Journal of Recent Sciences. 1. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/235769070_Using_ultrasonic_sensor_for_blind_and_deaf_persons_combines_voice_alert_and_vibration_properties
- ↑ T. Ifukube, T. Sasaki and C. Peng, "A blind mobility aid modeled after echolocation of bats," in IEEE Transactions on Biomedical Engineering, vol. 38, no. 5, pp. 461-465, May 1991. http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/stamp/stamp.jsp?tp=&arnumber=81565&isnumber=2674
- ↑ Bousbia-Salah, M., Bettayeb, M. & Larbi, A. J Intell Robot Syst (2011) 64: 387. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10846-011-9555-7
- ↑ Bousbia-Salah M., Fezari M. (2007) A Navigation Tool for Blind People. In: Sobh T. (eds) Innovations and Advanced Techniques in Computer and Information Sciences and Engineering. Springer, Dordrecht. https://link.springer.com/chapter/10.1007%2F978-1-4020-6268-1_59
- ↑ P. Mihajlik, M. Guttermuth, K. Seres and P. Tatai, "DSP-based ultrasonic navigation aid for the blind," IMTC 2001. Proceedings of the 18th IEEE Instrumentation and Measurement Technology Conference. Rediscovering Measurement in the Age of Informatics (Cat. No.01CH 37188), Budapest, 2001, pp. 1535-1540 vol.3. http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/stamp/stamp.jsp?tp=&arnumber=929462&isnumber=20096
- ↑ Pereira, A., Nunes, N., Vieira, D., Costa, N., Fernandes, H. & Barroso, J. (2015). Blind Guide: An ultrasound sensor-based body area network for guiding blind people. Procedia Computer Science, 67, 403–408. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procs.2015.09.285
- ↑ Bujacz, M., & Strumiłło, P. (2016). Sonification: Review of Auditory Display Solutions in Electronic Travel Aids for the Blind. Archives of Acoustics, 41(3), 401–414. https://doi.org/10.1515/aoa-2016-0040
- ↑ Mehta, U. Alim, M. Kumar, S. (2017). Smart path guidance mobile aid for visually disabled persons. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1877050917302089
- ↑ 27.0 27.1 Ram, S. Sharf, J. (2002). The people sensor: a mobility aid for the visually impaired. https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/abstract/document/729548
- ↑ 28.0 28.1 Cassinelli, A. Reynolds, C. Ishikawa, M. (2006). Augmenting spatial awareness with Haptic Radar. https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/abstract/document/4067727
- ↑ Lacey, G. Dawson-Howe K. (1998). The application of robotics to a mobility aid for the elderly blind. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0921889098000116
- ↑ Van Erp, J. Kroon, L. Mioch, T. Paul, K. (2017), Obstacle Detection Display for Visually Impaired: Coding of Direction, Distance, and Height on a Vibrotactile Waist Band. https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fict.2017.00023/full
- ↑ Park, H.-J., Lee, J. D., Kim, E. Y., Park, B., Oh, M.-K., Lee, S., & Kim, J.-J. (2009). Morphological alterations in the congenital blind based on the analysis of cortical thickness and surface area. NeuroImage, 47(1), 98–106. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2009.03.076
- ↑ Boekhorst, B, te. Kruithof, E. Cloudt, Stefan. Cloudt, Eline. Kamperman, T. (2017). Robots Everywhere PRE2017 3 Groep13. http://cstwiki.wtb.tue.nl/index.php?title=PRE2017_3_Groep13
- ↑ https://benselectronics.nl/hc-sr04-ultrasonic-module/