Mobile Robot Control 2024 Ultron:Solution 1: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| (2 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 16: | Line 16: | ||
#*The control loop continues executing as long as the robot is properly connected 'io.ok()' and the 'move ' flag is 'true'. | #*The control loop continues executing as long as the robot is properly connected 'io.ok()' and the 'move ' flag is 'true'. | ||
#*Once the 'move' flag is set to 'false' , the control loop stops executing, effectively halting the robot's motion.[[File:Execise1 Hao.png|thumb]] | #*Once the 'move' flag is set to 'false' , the control loop stops executing, effectively halting the robot's motion.[[File:Execise1 Hao.png|thumb]] | ||
Chuyu: | |||
Initialization: | |||
The IO object initializes the io layer. | |||
The Rate object helps keep the loop at a fixed frequency. | |||
Obstacle Detection: | |||
Laser data is continuously read within the control loop. | |||
If any distance measurement from the laser scan is less than 0.5, an obstacle is detected. | |||
Stopping Action: | |||
If an obstacle is detected: | |||
Different actions are taken based on the distance to the obstacle. | |||
If the obstacle distance is less than 0.2, the robot stops. | |||
Control Loop Condition: | |||
The loop continues executing as long as the robot is properly connected (io.ok() is true). | |||
[[File:Exercise1 Chuyu.png|thumb]] | |||
The loop also incorporates obstacle detection and stopping actions. | |||
'''Exercise 2: Testing your don't crash''' | '''Exercise 2: Testing your don't crash''' | ||
| Line 23: | Line 75: | ||
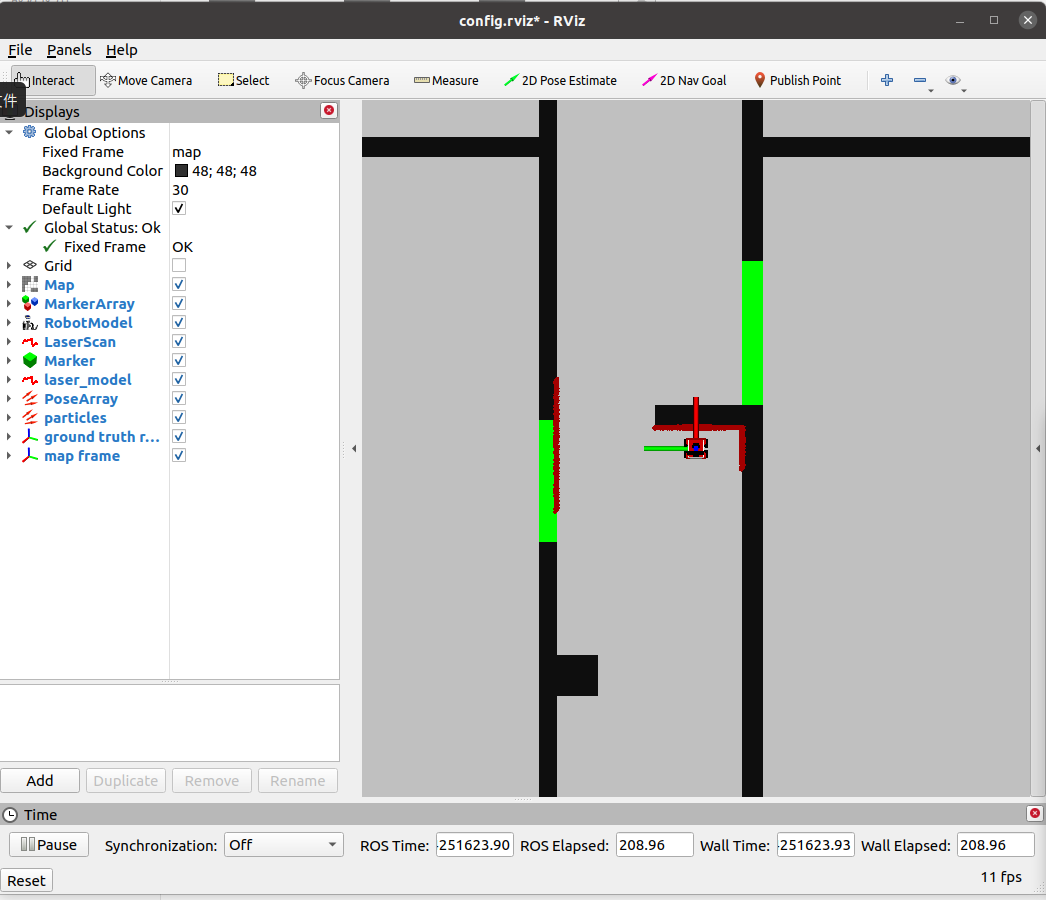
# [[File:Exercise2-1 Hao.png|thumb]]In map1 the robot can stop as the designed purpose. | # [[File:Exercise2-1 Hao.png|thumb]]In map1 the robot can stop as the designed purpose. | ||
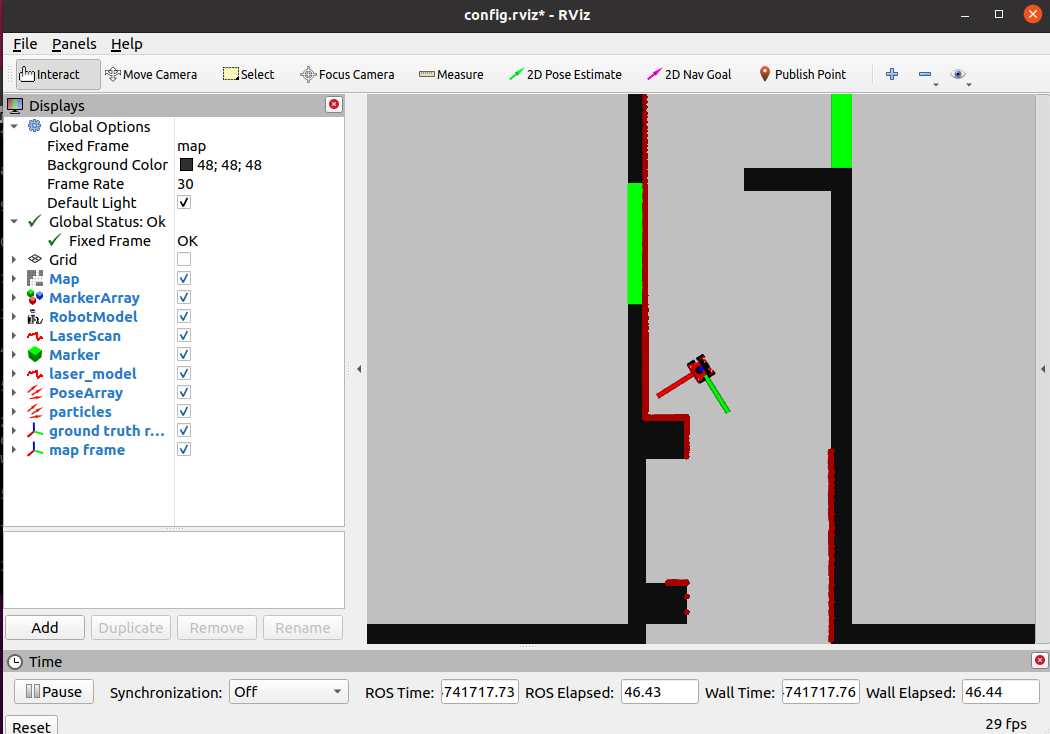
# [[File:Exercise2-2 Hao.png|thumb]]In map2 the robot stopped when detected the wall on the right side with distance<=0.2 | # [[File:Exercise2-2 Hao.png|thumb]]In map2 the robot stopped when detected the wall on the right side with distance<=0.2 | ||
Chuyu: | |||
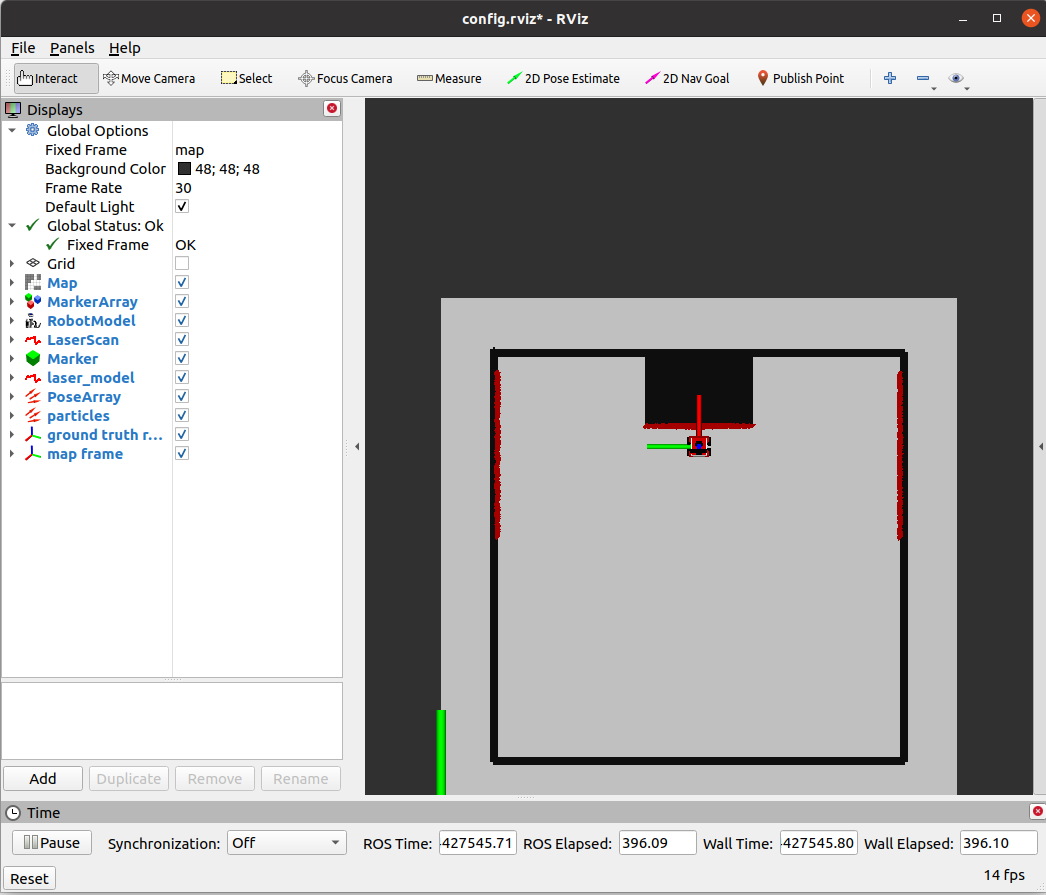
# In map 1, the robot keeps moving and does not collide with obstacles | |||
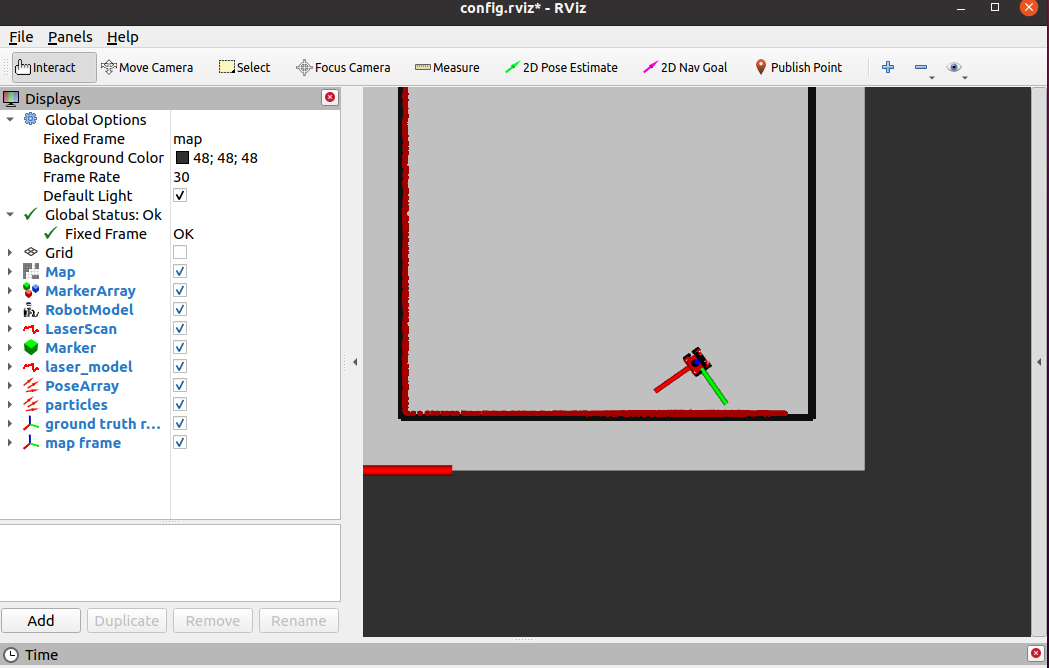
# In map 2, the robot keeps moving and does not collide with obstacles | |||
[[File:Exercise2-1 Chuyu.png|thumb]] | |||
[[File:Exercise2-2 Chuyu.png|thumb]] | |||
Revision as of 15:09, 3 May 2024
Exercise 1: the art of not crashing
Hao:
- Boolean Flag:
- A boolean flag named 'move ' is used to control whether the robot should continue moving or stop.
- It is initialized to 'true', indicating that the robot is initially allowed to move.
- Obstacle Detection:
- The program continuously reads laser sensor data inside the control loop.
- If any distance measurement from the laser scan is less than 0.2, an obstacle is detected.
- Stopping Action:
- When an obstacle is detected, the 'move ' flag is set to 'false'.
- Setting 'move ' to 'false' indicates that the robot should stop moving.
- Additionally, a stop command 'io.sendBaseReference(0, 0, 0)' is sent to the base controller immediately after detecting the obstacle.
- Control Loop Condition:
- The control loop continues executing as long as the robot is properly connected 'io.ok()' and the 'move ' flag is 'true'.
- Once the 'move' flag is set to 'false' , the control loop stops executing, effectively halting the robot's motion.
Chuyu:
Initialization:
The IO object initializes the io layer.
The Rate object helps keep the loop at a fixed frequency.
Obstacle Detection:
Laser data is continuously read within the control loop.
If any distance measurement from the laser scan is less than 0.5, an obstacle is detected.
Stopping Action:
If an obstacle is detected:
Different actions are taken based on the distance to the obstacle.
If the obstacle distance is less than 0.2, the robot stops.
Control Loop Condition:
The loop continues executing as long as the robot is properly connected (io.ok() is true).
The loop also incorporates obstacle detection and stopping actions.
Exercise 2: Testing your don't crash
Hao
- In map1 the robot can stop as the designed purpose.
- In map2 the robot stopped when detected the wall on the right side with distance<=0.2
Chuyu:
- In map 1, the robot keeps moving and does not collide with obstacles
- In map 2, the robot keeps moving and does not collide with obstacles