Embedded Motion Control 2017 Group 9: Difference between revisions
| Line 48: | Line 48: | ||
=== Requirements === | === Requirements === | ||
• PICO drives autonomously through maze<br> | |||
• Being able to take a turn without touching a wall <br> | |||
o Being able to detect a turn or branching corridor<br> | |||
o Avoiding collisions with obstacles (including the walls)<br> | |||
o Driving straight and rotating smoothly <br> | |||
• PICO should not stand still for 30 seconds<br> | |||
• Avoid getting trapped in a loop of the maze<br> | |||
• Being able to recognize the door<br> | |||
=== Functions === | === Functions === | ||
Revision as of 21:12, 15 May 2017
Group Members
| Name: | Student id: |
| Mian Wei | X |
| Zhihao Wu | X |
| Petrus Teguh Handoko | X |
| Bo Deng | X |
| Bo Cong | X |
| Jian Wen Kok | X |
| Nico Huebel | Tutor |
Initial Design
Requirements
• PICO drives autonomously through maze
• Being able to take a turn without touching a wall
o Being able to detect a turn or branching corridor
o Avoiding collisions with obstacles (including the walls)
o Driving straight and rotating smoothly
• PICO should not stand still for 30 seconds
• Avoid getting trapped in a loop of the maze
• Being able to recognize the door
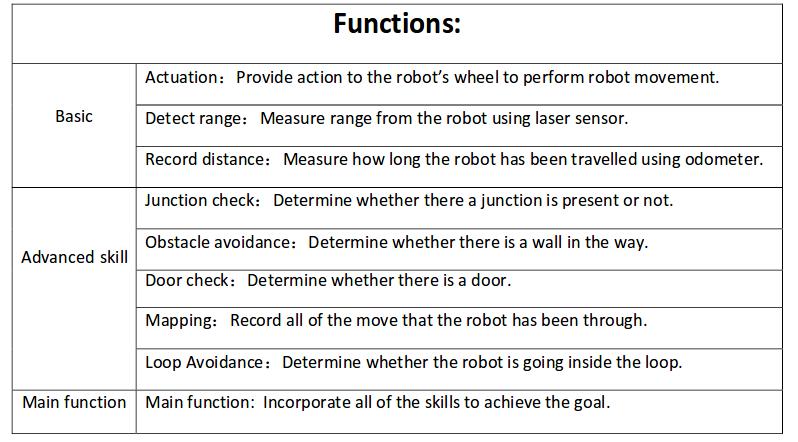
Functions
Components
drive control
‐Holonomic base (omni‐wheels)
‐Pan‐tilt unit for head
detection
‐170◦ wide‐angle camer
‐Laser Range Finder (LRF)
‐Wheel encoders (odometry)
‐Asus Xtion Depth sensor
world model
computer
‐Intel I7
‐Ubuntu 14.04
Specifications
- maximum translational speed of 0.5 m/s
‐ maximum rotational speed of 1.2 rad/s
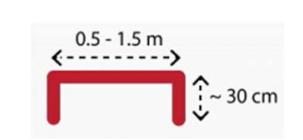
‐ Door template: length of 0.5 ‐ 1.5m and with side walls of approximately 30cm, see figure below
‐ LRF accuracy and range unknown
‐ odometer accuracy unknown
Interfaces
The odometer and LRF generates data for mapping the environment.
The algorithm sets nodes on the junction as a setpoint for navigation, plans the route and put the actuators to work accordingly.
The odometer and LRF keeps on keeping track of the environment and the software recognizes obstructions, dead ends that might be doors and junction.