Embedded Motion Control 2014 Group 8: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
== Group members == | |||
Harm van Deursen <br> | Harm van Deursen <br> | ||
Lex Hoefsloot <br> | Lex Hoefsloot <br> | ||
| Line 4: | Line 6: | ||
Teun Melief <br> | Teun Melief <br> | ||
Robin Smit <br> | Robin Smit <br> | ||
== PICO Knowns == | == PICO Knowns == | ||
| Line 57: | Line 58: | ||
== C++ coding == | == C++ coding == | ||
= Master = | === Master === | ||
...... [All] ...... | ...... [All] ...... | ||
= Driving straight = | === Driving straight === | ||
...... [Harm] ...... | ...... [Harm] ...... | ||
= Drive safely = | === Drive safely === | ||
...... [Robin] ...... | ...... [Robin] ...... | ||
= Detect a corner = | === Detect a corner === | ||
...... [Robin] ...... | ...... [Robin] ...... | ||
= Take the corner = | === Take the corner === | ||
...... [Robin en Paul] ...... | ...... [Robin en Paul] ...... | ||
= Arrow detection = | === Arrow detection === | ||
...... [Teun en Lex] ...... | ...... [Teun en Lex] ...... | ||
= Algorithm to solve the maze = | === Algorithm to solve the maze === | ||
...... [Paul] ...... | ...... [Paul] ...... | ||
Revision as of 11:10, 21 May 2014
Group members
Harm van Deursen
Lex Hoefsloot
Paul Verhoekx
Teun Melief
Robin Smit
PICO Knowns
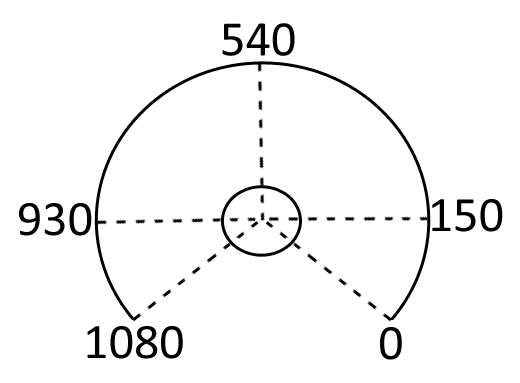
1. 1080 laser points for distance measurement
2. approximately 250 degrees of measurement direction
3. The datapoint at the left (930), front (540) and right (150)
4. The maximum distance measurement is 30 meters
5. ...
6. PICO's velocity and angular velocity can be determined. These are in meters per second and radians per second respectively.
7. ...
The figure on the right shows the location of the laser (distance) measurement points
First test
The first goal was to survive the corridor test. This means any corner, left or right, should be detected and taken without any collosion.
There were two main tactics to be tested;
Global tactic (inserted in both programs):
- The corner can be detected by either laser point #150 or #930.
- Safety (not hitting the wall) is inserted for the measurement points 150 - 250, 400 - 540, 540 - 680 and 820 - 970.
first tactic:
1. The distance in front is measured and saved when a corner is detected.
2. Than PICO starts rotating until the distance on the side where the corner has not been measured is equal to the distance that was previously in front
3. PICO drives sidewards until the distance is 30 centimeters less
4. pico drives straight ahead again. The corner is taken
Second tactic:
1. The corner is measured but PICO keeps on driving straight ahead and the timer starts
2. The end of the corner is detected and the timer stops
3. PICO drives backwards for half of the time the timer has measured
4. PICO drives sidewards through the corner
5. PICO turns to get back in its neutral position
Observations;
- All measurement points should be used for safety to ensure safety
- The big mess should be cleaned and divided into seperate files which will be included into the master file
- One point to measure a corner is not robust. This should be done by the use of more points.
However, the second tactic seems to work quite okay and will thus be used for the corridor competition
Corridor test
Unfortunately there was not enough time to implement the observations in the code. The second method is used and led to a time to pass the corridor in 32 seconds.
second test
................................
C++ coding
Master
...... [All] ......
Driving straight
...... [Harm] ......
Drive safely
...... [Robin] ......
Detect a corner
...... [Robin] ......
Take the corner
...... [Robin en Paul] ......
Arrow detection
...... [Teun en Lex] ......
Algorithm to solve the maze
...... [Paul] ......
It's a new world
How to load the T-junction:
- Open Terminator
- Run:
gazebo maze/placearrow_Tjunc.world
when in the maze folder - In another terminal
- Run:
rosrun maze spawn_Tjunc
- and run:
roslaunch pico_gazebo pico.launch
to load Pico - Now you can run Rviz:
rosrun pico_visualization rviz